Benign Breast Disease
Benign breast conditions or diseases (BBD) are noncancerous breast disorders of the breast which can occur in both women and men.
Types of BBD:
There are many types of benign breast conditions, usually termed as fibrocystic change.
Some common types of BBD are Fibroadenomas, Cysts and Hyperplasia.
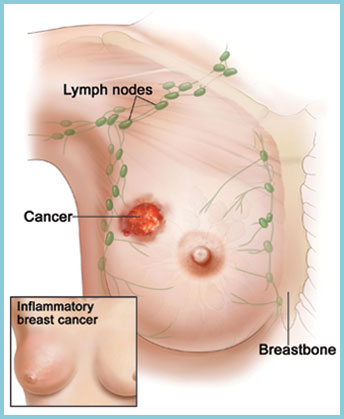
Breast Cancers
When breast cells divide and grow without their normal control. Breast tumors tend to grow slowly. Although, it can take up to 10 years to feel as a large lump but some tumors can aggressively grow much faster.